Explainers
Here’s all you need to know about HDR

The screen is the most important part of your smartphone, and serves as both display and interface. Over the past decade or so, we’ve been inundated with selling points like Retina Display, 720p, 1080p, 1440p, and even 4K. The latest buzzword for screens is high dynamic range or HDR, and the latest flagship phones tout it as a must-have spec.
But what is HDR in the first place?
More colors, more brightness
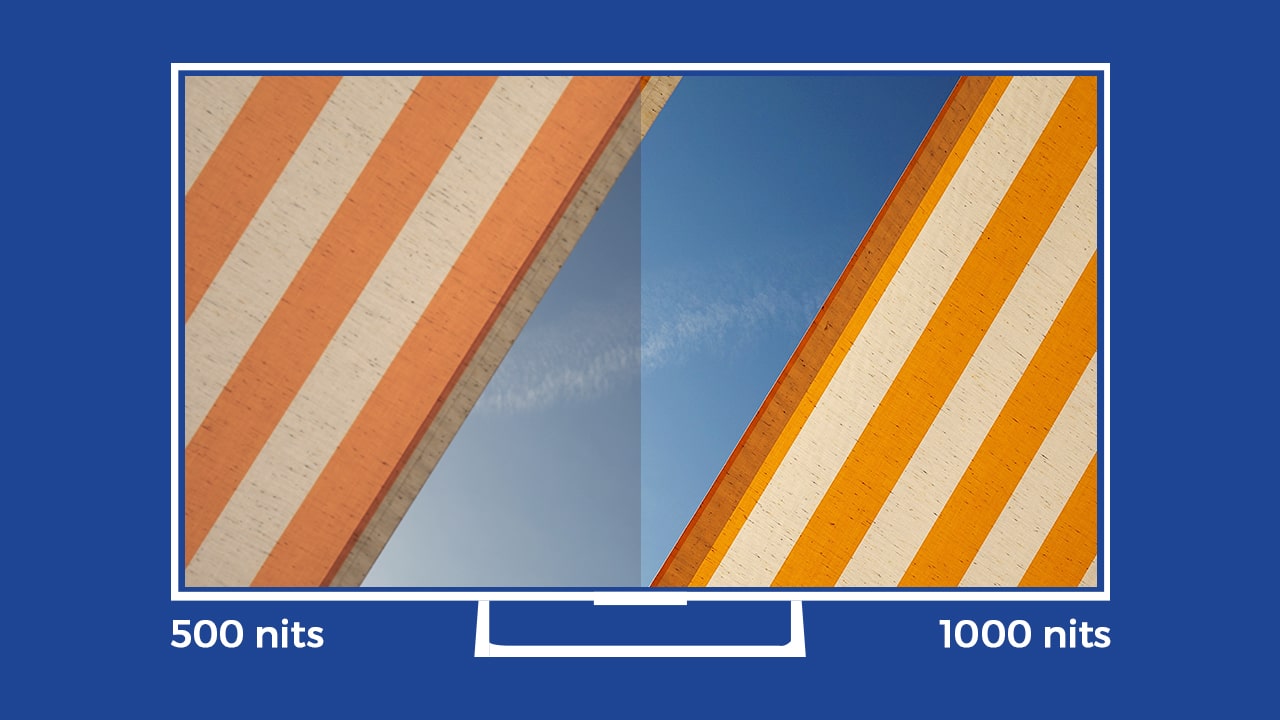
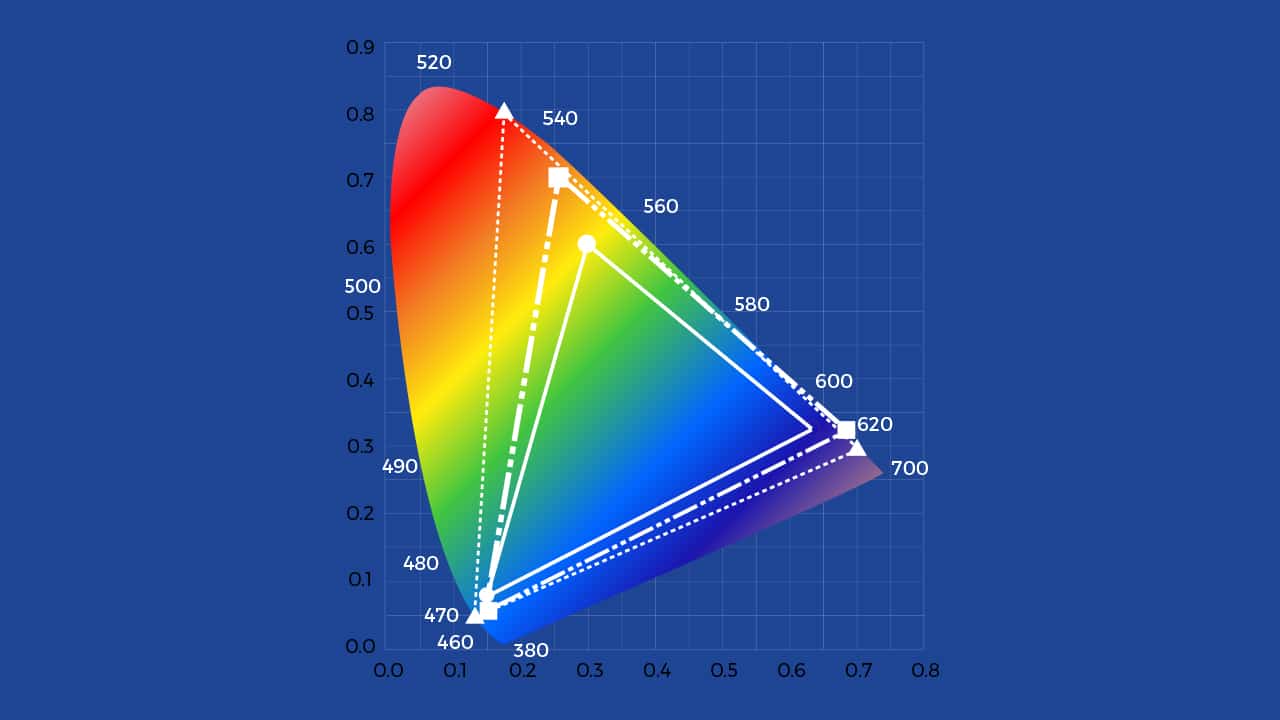
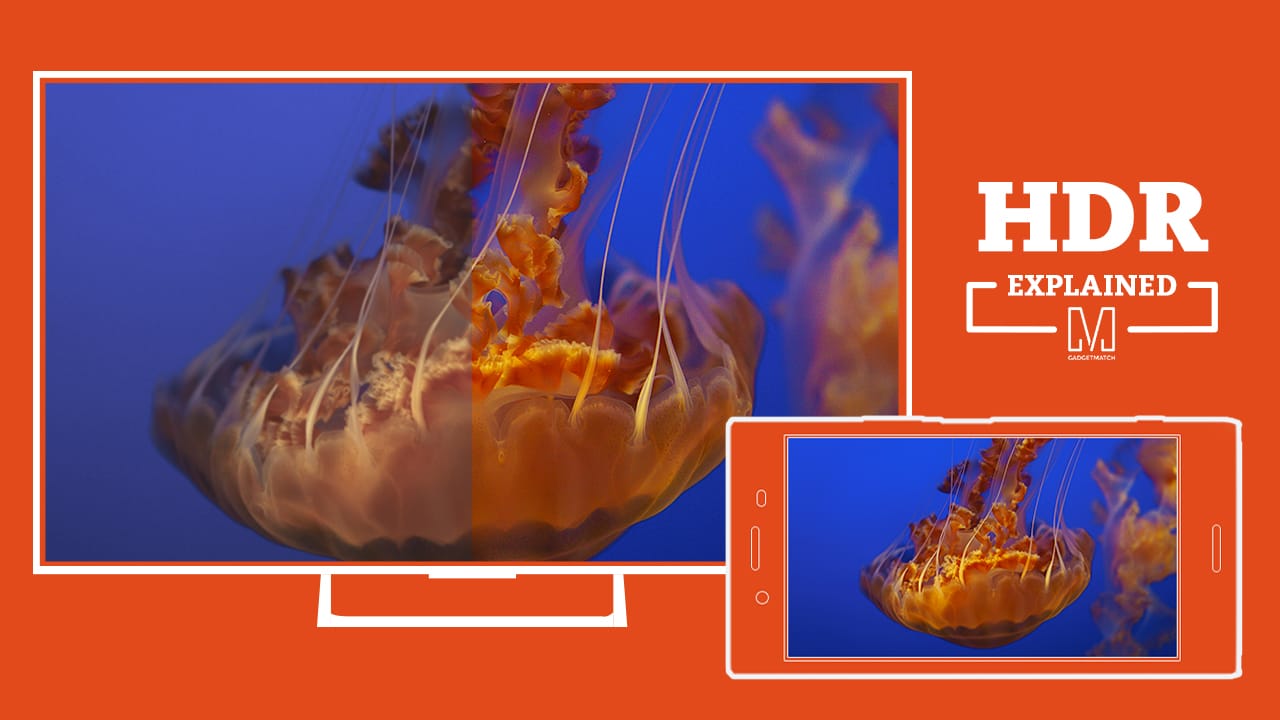
Put simply, HDR lets your display exhibit a far wider range of colors. How? First, whites are whiter, and blacks are blacker. The screen does this by being much brighter than what you’re normally used to, to the tune of 1,000 nits (a unit used for display brightness). By comparison, your old flagship phone probably topped out at around 500 nits. An HDR display can also illuminate or darken specific areas of the screen, whereas a non-HDR display commonly lights the entire screen evenly.
Second is wide color gamut, or WCG. This feature increases both the color palette (the number of colors available and the bit depth (or the number of shades of those colors). Your old phone could display nearly 17 million colors. By contrast, an HDR display can show over a billion, which is much closer to what you can see in real life. When working in tandem, these two processes enable the screen to show a range of colors that are more akin to real life. This is why people who have seen an HDR display liken it to looking out a window.
But there lies the problem. The most difficult issue with conveying what HDR is exactly is that if you don’t actually have access to an HDR-capable display, it’s impossible to show the difference. Conversely, if you have an HDR display and a non-HDR display side by side, the improvements are instantly evident. This technology represents a generational leap, much like the jump from black-and-white to color, or standard definition to high definition.
A feature by any other name
You’ve probably heard the abbreviation “HDR” before as a vaunted feature for smartphones even before it was used for displays. Another source of confusion is that HDR also applies to another selling point for phones: the HDR feature of a camera. In camera HDR, the camera takes many exposures of the same scene and combines them, thereby showing all of the subtle steps in highlights and shadows.
The principle between HDR displays and photography remains roughly the same, with the end result being an image that has higher contrast and more colors. Crushed blacks and blown-out whites are also eliminated as a result. This is where the phrase “high dynamic range” comes in, representing the difference between the darkest parts of an image with the lightest.
Which gadgets have HDR?
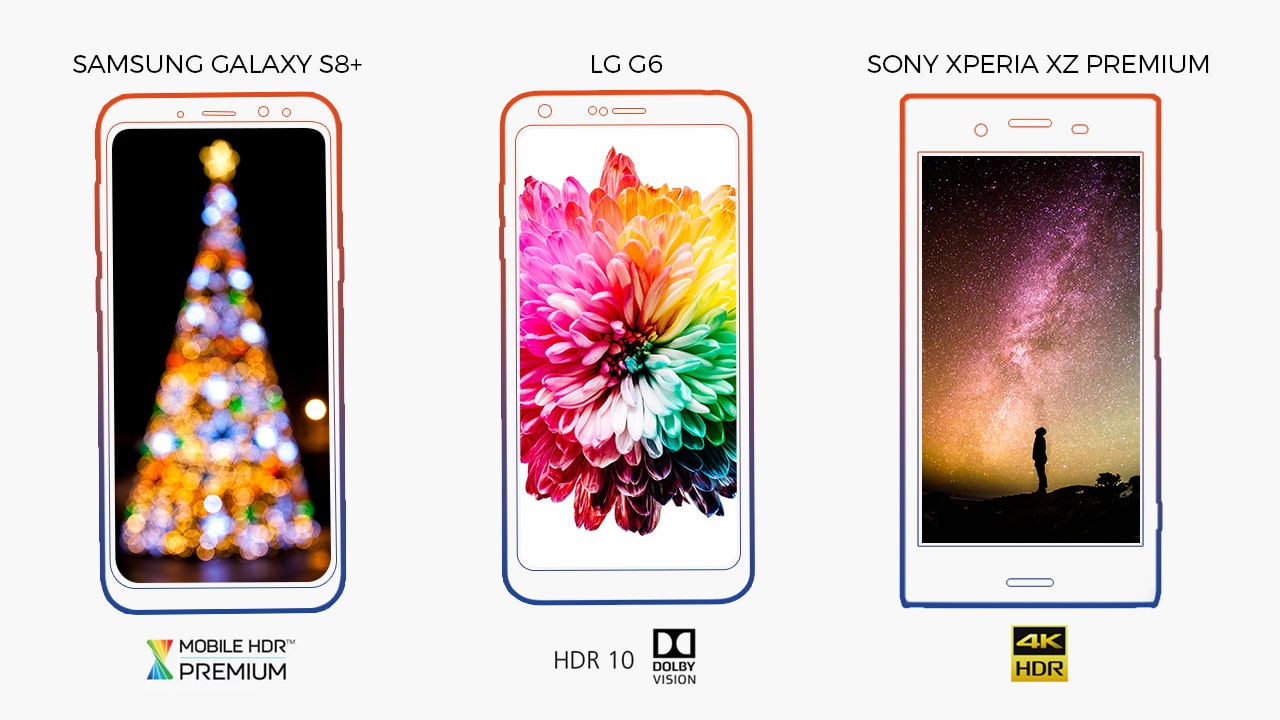
All of this year’s important flagship phones have HDR-enabled displays, including the LG G6 and the Sony Xperia XZ Premium. However, these phones appear to be using different standards for what constitutes HDR — the LG G6 uses both the open HDR10 standard and proprietary Dolby Vision, and Sony’s 4K phone appears to be using its own definition of HDR.
Hopefully, HDR specifications normalize in subsequent generations of phones. You wouldn’t want to get a phone with HDR to find out that your HDR content won’t even display properly on it. Thankfully, at this year’s Mobile World Congress, the Ultra HD Alliance announced Mobile HDR Premium, which is an HDR standard specifically developed for smartphones, tablets, and laptops. The Samsung Galaxy S8 and S8+, two of the best phones of 2017, were the first pair to adhere to this certification.
Here are the specifics of Mobile HDR Premium for a wide variety of portable devices:
| Device | Resolution | Dynamic Range | Color Space | Bit Depth |
| Smartphones (3- to 7-inch screens) | 60 pixels/degree | .0005-540 nits | 90% of P3 Color gamut | 10 |
| Tablets (7- to 12.9-inch screens) | 60 pixels/degree | .0005-540 nits | 90% of P3 Color gamut | 10 |
| Laptops (9.5- to 18-inch screens) | 60 pixels/degree | .0005-540 nits or 0.1-600 nits | 90% of P3 Color gamut | 10 |
Why do you need HDR?
If you’re after the top-end phones, you’ll find it increasingly difficult to avoid HDR. The benefits that a more accurate display brings is most useful if you’ll be doing image work on your phone, like quickly editing photos on VSCO before sharing it to the ether. But its advantages will also be immediately noticeable if you consume content on your phone (like most people do). More and more media providers are putting out HDR content —YouTube, for one, has had HDR support since last year, and both Netflix and Amazon Video have it as well.
And with diminishing returns in terms of resolution on a five- to six-inch screen (do you really need 4K on a screen as big as your palm?), HDR is one display buzzword that is instantly apparent. Plus, unlike a 4K screen that eats batteries for breakfast, HDR on your phone can actually extend your phone’s longevity; the dynamic and selective adjustment of brightness, depending on what’s shown, should increase your screen-on time by a significant amount.
SEE ALSO: What exactly is Fast Charging? And how does it work?
[irp posts=”14641″ name=”What exactly is Fast Charging? And how does it work?”]


It’s that time of the year again!
Since 2020, Samsung has equipped the Galaxy S20 Ultra with an ultra-fast 45W fast-charging speed compared to the Galaxy S10+‘s measly 15W charging standard. Four years after, 45W still remained on the Galaxy S24 Ultra.
For three consecutive years, Michael Josh has conducted a dedicated charge test to know whether its 45W “Super Fast Charging” works as promised on the latest line of Samsung’s Galaxy flagships. The Galaxy S24 Ultra isn’t an exemption to that.
Curious to know? Find out in our Galaxy S24 Ultra and Galaxy S24+ Charge Test.
Explainers
ChatGPT Explained: Should we be scared of AI?
Will the talking robot take over the world?

Back in the earlier days of the internet, an emerging but short-lived trend involved chatbots who could generate conversation with whomever it talked to. Does this sound familiar? Today, a similar phenomenon is creating a lot of waves online, headed by the infamous ChatGPT. The exceedingly popular ChatGPT is turning heads out of fear that the technology will eventually upend society and eradicate a lot of jobs.
But what exactly is ChatGPT? How is it different from language programs in the past? Is the world right to worry about them?
On the rise of language learning
ChatGPT is hardly the first software to inexplicably generate comprehensible dialogue without human intervention. Decades ago, the internet hosted rudimentary versions of today’s chatbot technology. The concept is somewhat similar, though. The early versions relied on a database of responses from human users. If you asked about coffee, for example, the answer you get will likely come from the logs of another user who talked about coffee in the past.
Because the system was imperfect in its infancy, part of the appeal was trying to get the software to fumble a conversation. However, if it did mess up, you can count on it asking you what it should have said. The next time someone asks the same question, the software might mirror what you said, creating a learning process between the software and the user.
Today, chatbots — meaning those usually used by businesses today — operate in the same way. If a customer comes with a query, the software will rely on a set of responses to most appropriately address the user’s problem. If the software can’t come up with a solution, the ball usually gets passed on to a human consultant.
Is ChatGPT just another chatbot?
Though the label certainly gets thrown around, ChatGPT isn’t strictly a chatbot. Instead, the software uses GPT-3.5, a specific language model created by OpenAI. Whereas early and more rudimentary versions of the same technology can already store an unbelievable amount of information in its memory, ChatGPT can analyze billions of words and the relationship between them.
Further, OpenAI extensively trains the software, ensuring that comprehension and grammar can live up to today’s standards. The learning is supervised. In fact, the company even has a makeshift reward system to ensure that the software puts out the most appropriate response. With users also contributing to the software’s learning process, ChatGPT is quickly emerging as a powerhouse for the technology.
The results speak for themselves. While users can generate simple conversations with the software, ChatGPT can just as easily answer more extensive queries with lengthier responses. If you ask it to create an essay about Christopher Columbus, for example, it can write a lengthy piece that can easily fool a casual reader. It can even handle more speculative queries. In a sample published by the developer, ChatGPT can answer what would happen if Columbus discovered America in 2015.
What’s it good for?
Based solely on what the software can do, ChatGPT can find its purpose in today’s world. The software can improve voice assistants and chatbots all over the internet. It can make big strides in the world of automation, enabling a more responsive interface between user and software.
On a more human aspect, the software can also handle more professional jobs with simpler prompts such as those involving simple marketing copy. It can help with more ephemeral research efforts, allowing users to get simple answers for otherwise complex questions.
And, on a more technical side, ChatGPT can reportedly analyze and detect what’s wrong with a piece of coding. With the software, developers can use ChatGPT to potentially repair code without having to pore over every single line. Allowing a powerful tool to inspect code speaks volumes for a lot of applications all over the world including smart vehicles and technical machinery.
However, as with every piece of technology, users will always find a way to use something beyond what it was originally designed for. ChatGPT is now changing the world of education as students are using the software to do their homework for them. Though a lot of the sample texts look like they can fool only lower levels of education, a Wharton business school professor (via Business Insider) recently stated that he would have been fooled by a ChatGPT essay, grading a sample with a passable grade of B or B-.
Should we be scared of ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is undoubtedly rocking the world of education. While some schools have banned the technology outright, others are debating on the software’s impact on how schools are taught. Since ChatGPT deals out more factual information, could education reinvent itself to teach more personal, tailored learning, rather than just the ability to spit out memorized facts. (“Factual” might even be an exaggeration. CNET, which recently experimented with AI-written articles, discovered a plethora of errors from using the software.)
Now, education isn’t the only world in peril. The creative industry is facing an extreme challenge wherein ChatGPT can potentially cause workers their jobs. Though the danger certainly seems real, the limitations of technology are also real. ChatGPT can create comprehensible text that can fool a human, but it will likely stumble with conceptualization.
A piece of software is just software. Even if it can write an essay about existentialism, it cannot think of the concept metaphysically. In the same way, even if it can show you a photo of a parrot, it cannot think of that photo as anything but a pattern of pixels. To a language learning software, words don’t mean anything else besides their relationship with each other. It’s the same thought process as a dog learning to run to its human when its name is called. The dog doesn’t know that you just said its name (or even the mere concept of a name); it just knows to do a certain action after hearing a specific sound.
Can ChatGPT change the world? Overall, the jury is still out, but it’s unlikely that a piece of learning software can do much to replace human-centric work. Regardless, it’s important to think of how ChatGPT can improve (or detriment) humanity.
Like with other supposedly dangerous technology, the world of technology is a Pandora’s box. We can never put the genie back into the bottle. Once it’s out, it’s out. Instead of worrying about how technology can destroy the world, the more appropriate response is to figure out how it can better humanity without sacrificing anyone’s wellbeing in the process.

When you’re looking to buy a new device, which specs should you pay attention to? Which upgrades should you consider?
In this video instead of reviewing the latest new smartphone, we’re going to talk about its unsung hero: RAM.
We partnered with @MicronTech to help you understand all the magical things that you get to do on your smartphone thanks to internal memory and storage.
To find out more about Micron’s mobile memory and storage solutions and how they’re bringing mobile innovation to life, visit https://www.micron.com/solutions/mobile or watch our explainer video.
-

 Accessories2 weeks ago
Accessories2 weeks agoApple Vision Pro Review: Two Months Later
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoFortify your home office or business setup with these devices
-

 Gaming1 week ago
Gaming1 week agoThe Rogue Prince of Persia looks like an ultra-colorful roguelite
-

 Events1 week ago
Events1 week agoStellar Blade: PlayStation taps cosplayers to play Eve for game’s launch
-

 Gaming1 week ago
Gaming1 week agoStar Wars Outlaws release date revealed
-

 Accessories1 week ago
Accessories1 week agoLogitech unveils G Pro X 60 gaming keyboard: Price, details
-

 Philippines2 weeks ago
Philippines2 weeks agovivo Y100 to release in Philippines on April 27
-

 Deals2 weeks ago
Deals2 weeks agoSamsung Awesome April: Deals on Galaxy A series